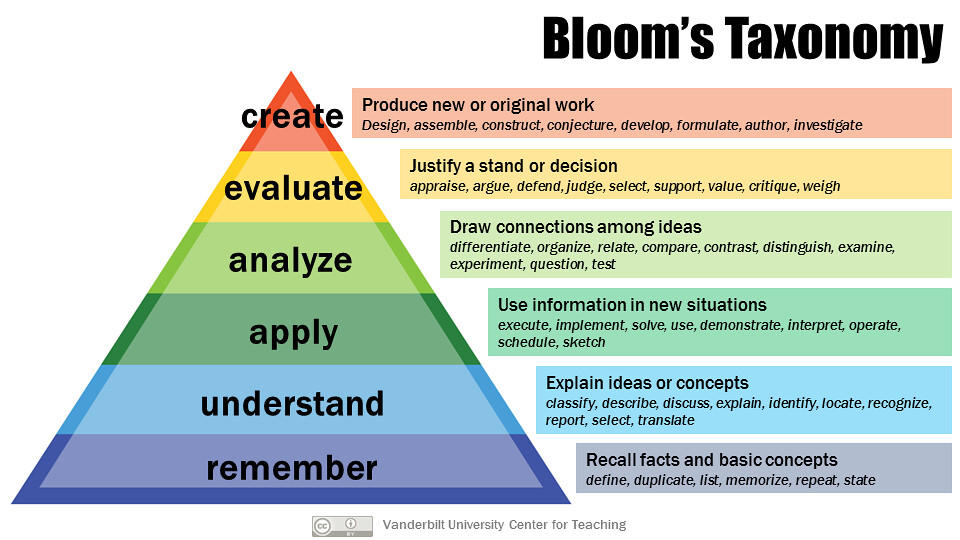
Created in 1956, the Bloom’s Taxonomy framework has been applied by generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching. The taxonomy is popularly remembered according to the six main categories: Knowledge, Comprehension, Application, Analysis, Synthesis, and Evaluation.
In 2001, a group of cognitive psychologists, curriculum theorists and instructional researchers, and testing and assessment specialists published a revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy, pointing to a more dynamic conception of classification. Action words described the cognitive processes by which thinkers encounter and work with knowledge.
The prevalence of digital technologies, communication tools, and assorted media requires some consideration of how course objectives and activities evolve. Churches (2008) proposed a Digital Taxonomy, which is provided in this embedded Google Document:
Download the Google Doc as a PDF.
References
Armstrong, P. (n.d.). Bloom’s taxonomy. Vanderbilt University Center for Teaching. Retrieved from https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/blooms-taxonomy
Churches, A. (2008). Bloom’s taxonomy Blooms digitally. Tech & Learning. Retrieved from https://www.techlearning.com/news/bloom39s-taxonomy-blooms-digitally
TeachThought (2017). 126 Bloom’s Taxonomy verbs for digital learning. Retrieved from https://www.teachthought.com/critical-thinking/126-blooms-taxonomy-verbs-digital-learning